Recently I tried migrating a SQL Server LocalDB to Azure and found what I thought would be an easy job, to actually be a bit pf a pain.
I’m not saying this is the best way to get a LocalDB live on Azure but below is the easiest way I could find, if anyone knows a better way, please feel free to let me know.
Why LocalDB
Usually I wouldn’t choose to develop against a LocalDB database but I had started my site with a Visual Studio template MVC site and thats what it gave me.
Moving to Azure
Now this is what I thought would be the easy bit. My local prototpye had gone well, so lets get this bad boy live! LocalDB is just a mdf and a ldf file like any SQL database, so I didn’t foresee any issues.
However, the only way I could find in Azure to upload an existing database was to use a .bacpac file.
SQL Server Management Studio
I couldn’t figure out a way of getting the .bacpac file directly from LocalDB or from within Visual Studio. The easiest way I could think of was to attach the mdf file to a local of instance of SQL Server. The fact that I didn’t have a local instance and had to set one up was a bit annoying.
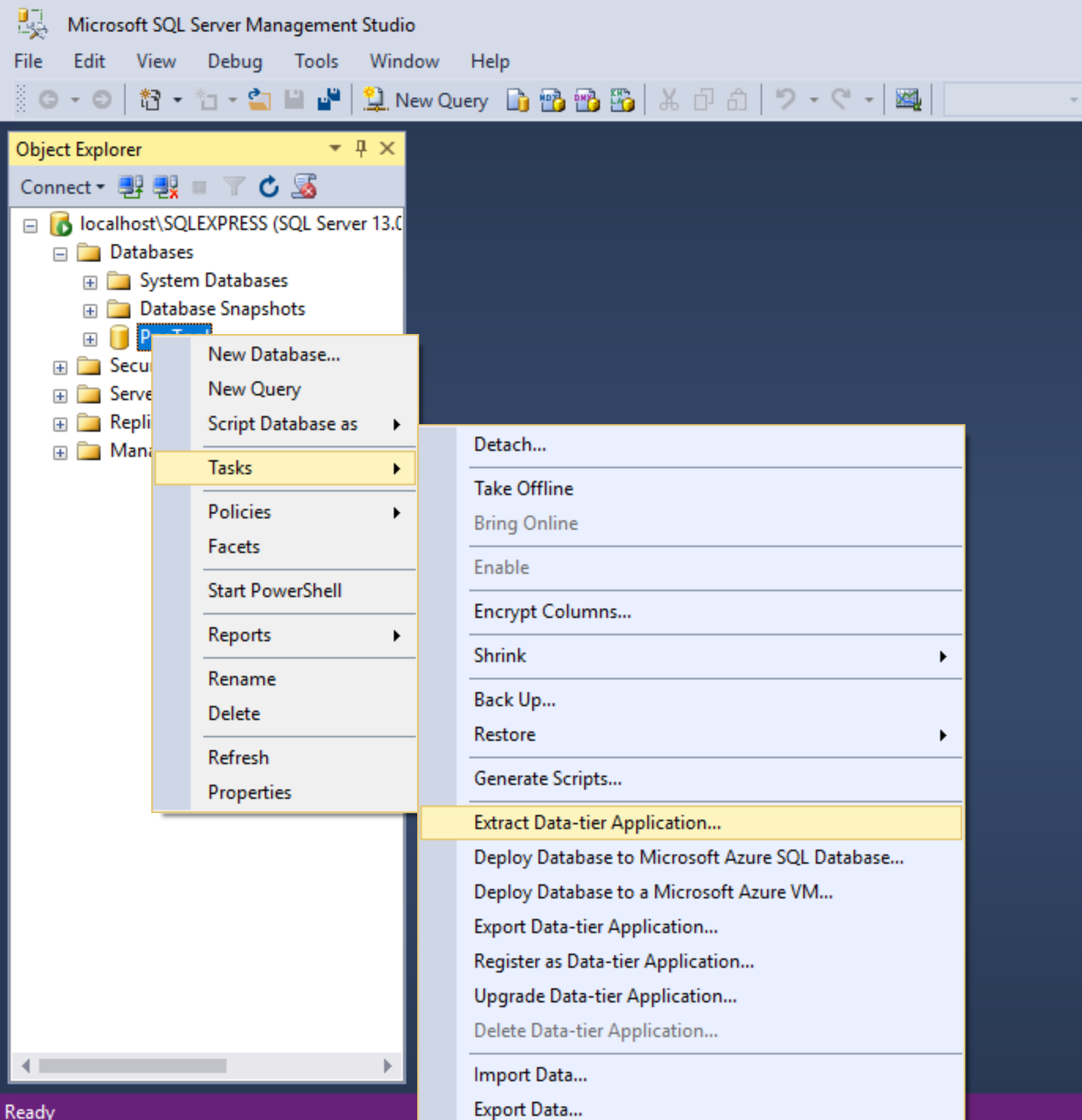
Export Data Tier Application
In order to get the .bacpac file, you need to select Export Data Tier from the Tasks menu of the database. You can select a local drive or upload the .bacpac directly to an Azure storage account. Bear in mind, that using this method you will need an storage account. Even if you store the .bacpac locally, you will need to upload to a storage account first in order to restore to an Azure SQL server.
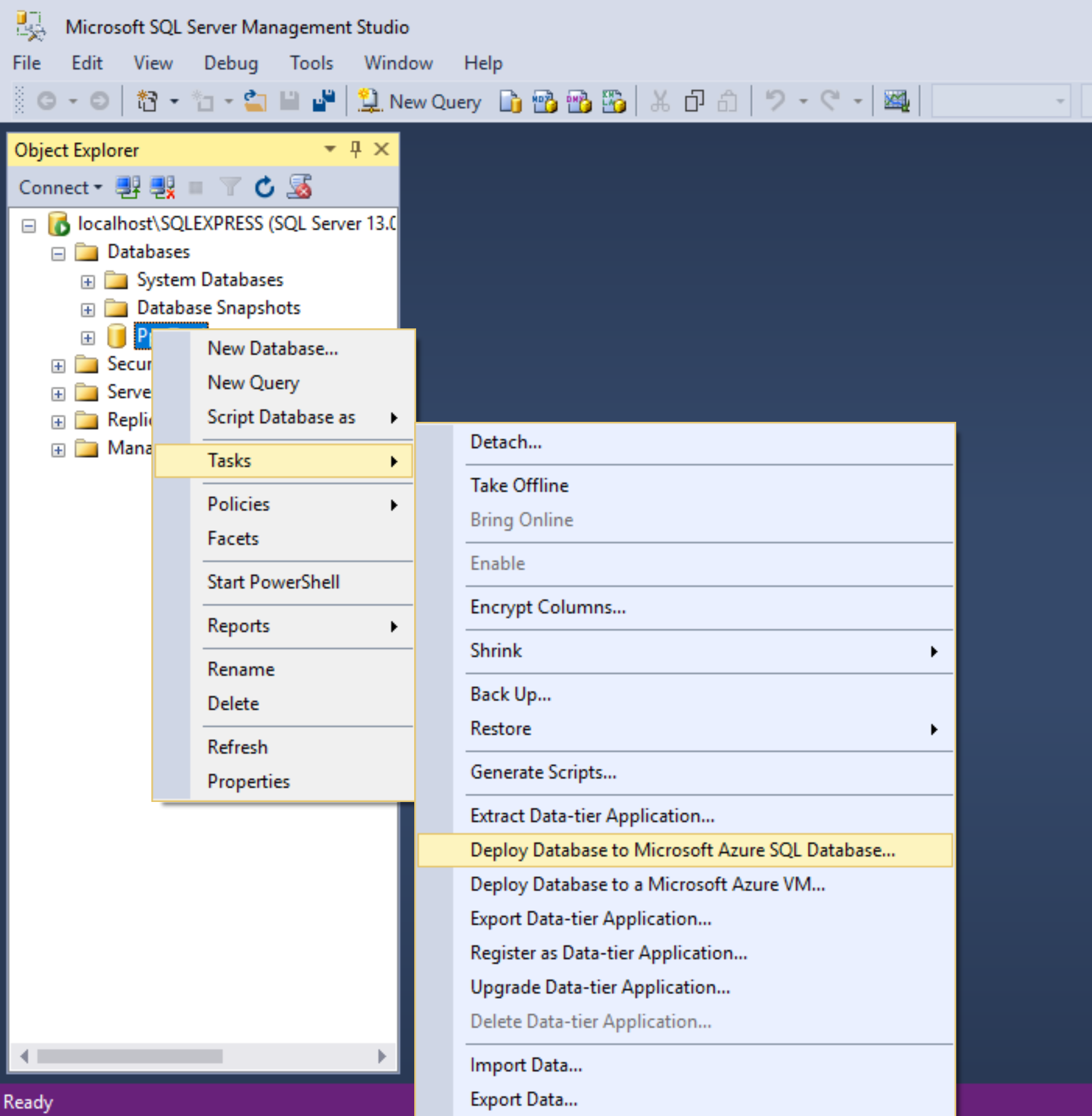
Deploy Database to Microsoft Azure SQL Database
The option I went for was Deploy Database to Microsoft SQL Database. With this method you do however need a connection string to an existing Azure SQL server. In order to get this, I made a free small database using the Azure portal, which creates an Azure SQL server at the same time as the database.
With the connection string you can then import the database directly. Once the import is finished, then you can delete the first database.
Generate Scripts
Another option would be to use the Generate Scripts task. However, this would also require attaching the LocalDB to a local instance of SQL Server.
By default, gnerating the scripts of a database will only generate the scripts for the schema.
If you also want to deploy the data in your database, don’t forget to select “Schema and data” from the advanced scripting options in the Generate Scripts wizard.
I was surprised at how awkward it was to transfer a LocalDB from a local prototype to Azure. There are a few different options to getting it done, it really depends on what you currently have set up in Azure for which one will be easiest for you.
And these are just the ways that I found, if anyone has any easier/quicker methods it would be great to hear them.